Understanding Eczema: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Treatments
Eczema or also known as atopic dermatitis is one of the most prevalent skin diseases that plague millions of people throughout the world. Symptoms of this condition are itchiness, inflammation of the skin that can cause distress and at times can interfere with the individual’s ability to go about their daily routine. Eczema is mostly common in children but can affect anyone of any age and the problem may continue well into adulthood. This article will therefore aim at informing the reader on what eczema is, its causes, symptoms and the remedies that can be taken in order to treat this skin condition.
What is Eczema?
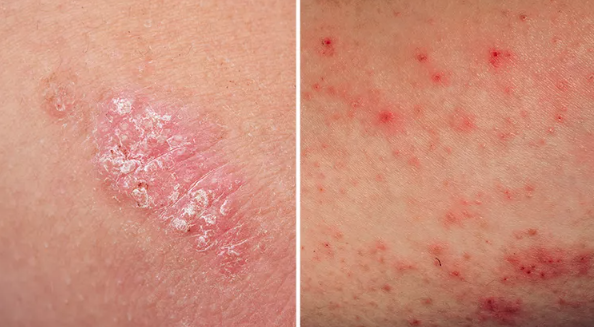
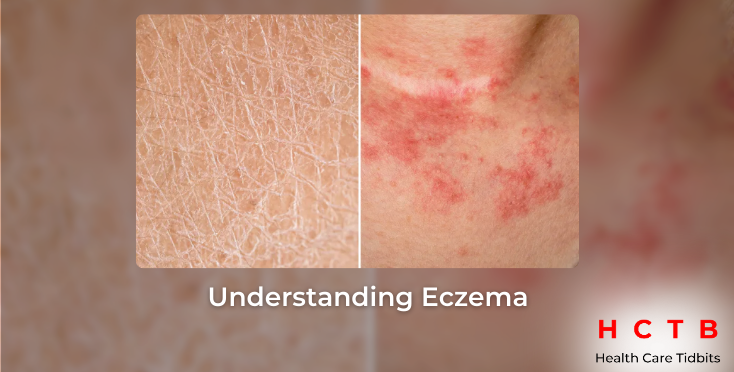
Eczema is a skin disease that characterizes itself by causing development of patches on skin and these patches display dryness, itching, inflammation and redness. It is most commonly observed on the areas of the skin that experiences a great deal of friction like the face, hands, feet and areas behind our elbows and knees. It is a chronic condition, and it is capable of recurring from time to time particularly when one is subjected to some form of stimuli. Eczema is not a communicable disease, but it quite affects a person’s quality of life.
Causes of Eczema
The exact cause of eczema is not fully understood, but several factors contribute to the development of this skin condition:
- Genetics: If you have a family history of eczema, asthma, or hay fever, you are more likely to develop eczema. This genetic link means that the skin barrier is weaker, making it less effective at retaining moisture and protecting against irritants.
- Immune System Dysfunction: In people with eczema, the immune system overreacts to certain allergens or irritants, causing inflammation and flare-ups.
- Environmental Factors: Common triggers include pollen, dust mites, pet dander, and harsh weather conditions. Dry air or exposure to chemicals in detergents, soaps, and lotions can aggravate the skin.
- Stress: Emotional stress can lead to eczema flare-ups as it weakens the immune system and makes the skin more reactive.
- Food Allergies: Some people with eczema may experience flare-ups after consuming certain foods, such as dairy, eggs, or nuts.
Common Symptoms of Eczema
Eczema symptoms can vary from person to person, but common signs include:
- Itchy Skin: The itching is often intense and worsens at night, leading to difficulty sleeping.
- Red or Brownish Patches: These patches commonly appear on the hands, feet, neck, and other areas prone to bending, such as the elbows and knees.
- Dry, Scaly Skin: The affected skin may become very dry, cracked, or even bleed.
- Thickened Skin: Constant scratching and rubbing can cause the skin to thicken and become leathery over time.
- Small, Fluid-Filled Blisters: In more severe cases, blisters may form, which can ooze and crust over.
Eczema tends to flare up and then improve, often triggered by environmental changes or contact with irritants.
Types of Eczema
Though atopic dermatitis is the most common form, there are other types of eczema that affect different parts of the body:
- Contact Dermatitis: Triggered by contact with irritants or allergens, such as certain soaps or metals.
- Dyshidrotic Eczema: Characterized by small, itchy blisters on the hands and feet.
- Nummular Eczema: Appears as circular, coin-shaped patches of irritated skin.
- Seborrheic Dermatitis: Affects oily areas of the body, such as the scalp, causing dandruff and scaly patches.
- Stasis Dermatitis: Occurs in the lower legs due to poor blood circulation, leading to swelling and redness.
How is Eczema Diagnosed?
Eczema is typically diagnosed based on the appearance of the skin and a patient’s medical history. A dermatologist may perform patch tests to identify potential allergens or irritants that trigger flare-ups. In some cases, a skin biopsy may be necessary to rule out other skin conditions.
Treatment Options for Eczema
Although there is no cure for eczema, various treatments can help manage symptoms and reduce flare-ups:
1. Moisturizing
Keeping the skin hydrated is crucial for managing eczema. Moisturizers help lock in moisture and create a protective barrier on the skin. Choose fragrance-free, hypoallergenic moisturizers and apply them immediately after bathing to seal in moisture.
2. Topical Steroid Creams
Steroid creams or ointments are commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation and itching during flare-ups. However, they should only be used under a doctor’s supervision, as long-term use can thin the skin.
3. Antihistamines
Oral antihistamines can be helpful in reducing itching, especially at night. They work by blocking the action of histamine, a chemical in the body that contributes to allergic reactions.
4. Prescription Medications
For moderate to severe cases of eczema, doctors may prescribe oral or injectable medications that suppress the immune system’s overreaction, such as cyclosporine or dupilumab. These drugs help reduce inflammation and control symptoms.
5. Phototherapy
Phototherapy, or light therapy, involves exposing the skin to controlled amounts of natural or artificial ultraviolet light. It can be effective in reducing inflammation and itching in patients who don’t respond well to other treatments.
6. Avoiding Triggers
Identifying and avoiding triggers is crucial for preventing eczema flare-ups. This may involve switching to hypoallergenic personal care products, wearing soft, breathable clothing, and reducing exposure to allergens like dust and pet dander.
Natural Remedies for Eczema
In addition to medical treatments, some natural remedies may help soothe eczema symptoms:
- Oatmeal Baths: Colloidal oatmeal can soothe inflamed skin and relieve itching.
- Coconut Oil: This natural oil has moisturizing and anti-inflammatory properties that may help reduce eczema symptoms.
- Aloe Vera: Known for its soothing and healing properties, aloe vera gel can calm irritated skin.
- Tea Tree Oil: Some studies suggest that tea tree oil has antimicrobial properties that may help prevent infections in eczema-affected skin.
Can Eczema Be Prevented?
While eczema cannot be cured, certain steps can be taken to reduce the risk of flare-ups:
- Moisturize Regularly: Keeping the skin well-hydrated is essential for maintaining the skin’s protective barrier.
- Use Gentle Skincare Products: Opt for mild, fragrance-free soaps and lotions that are less likely to irritate the skin.
- Avoid Harsh Fabrics: Wear soft, breathable fabrics like cotton and avoid scratchy materials like wool.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps keep the skin hydrated from within.
- Manage Stress: Since stress can trigger flare-ups, practicing relaxation techniques like meditation and deep breathing can be beneficial.
Living with Eczema
Certainly, the life with eczema is not easy, however if people know about the disease and its causes, they can easier cope with their problems. In fact, when they follow the right skin care, treatment, and changes their lifestyle, one can lead a normal happy life. Anyways, if you or your near one is suffering from eczema, it is highly advisable to go and consult a dermatologist to get professional advice and suggestions.